Last updated: June 26, 2024
3 mins read
What is estradiol?
Estradiol (E2), a type of estrogen hormone, is naturally produced by both males and females. In females, estradiol regulates the menstrual cycle, plays a role in fertility and ovulation, and can indicate the presence of PCOS. In males, this hormone is important for modulating libido, erectile function, and sperm synthesis. Estradiol also operates beyond the reproductive system, including bone health and brain function.
Why is estradiol important?
Estradiol levels provide insight into reproductive health and overall hormonal balance:In females: Elevated estradiol may indicate pregnancy, ovulation, PCOS, ovarian tumors, or liver disease. Low levels may suggest menopause, premature ovarian failure, or pituitary/adrenal dysfunction. Estradiol deficiency is strongly linked to osteoporosis.In males: High estradiol is associated with erectile dysfunction, loss of muscle mass, fatigue, mood changes, abdominal obesity, gynecomastia (enlarged breasts), cardiovascular disease, and insulin resistance. Low levels can cause decreased libido and reduced sexual activity.
How can I better understand my estradiol levels?
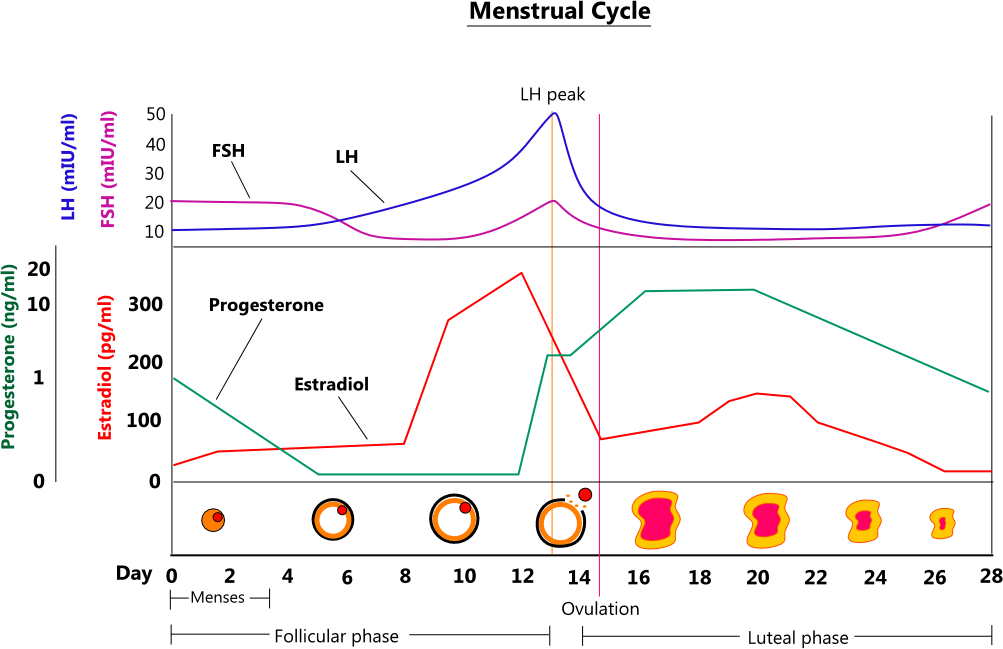
- Menstruating females: Test on day 3 of your menstrual cycle for baseline levels. Estradiol fluctuates significantly throughout the cycle, peaking during ovulation.
The following graph by Straight Healthcare shows how variable estradiol can be for menstruating females, along with other hormones that are important for the regulation of the menstrual cycle.
- Postmenopausal females: Levels remain consistently low with minimal fluctuation.
- Males: Levels are naturally low and relatively stable.
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT): If you’re on HRT, levels will reflect your treatment regimen.
Reference Ranges:
- Out of range (low): <10 pg/mL
- In range: 10-47 pg/mL
- Out of range (high): >47 pg/mL
How can I maintain optimal estradiol levels?
- Diet: Consume phytoestrogen-rich foods (soy, flaxseeds, sesame seeds, fruits, whole grains, nuts, vegetables) and ensure adequate intake of boron, B vitamins, vitamin D, and vitamin E
- Supplements: Consider black cohosh, DHEA, or red clover (consult your physician first)
- Body composition: Reduce body fat percentage (adipose tissue produces estrogen)
- Lifestyle: Manage stress, limit alcohol consumption, and exercise regularly
- Diet: Reduce processed foods and focus on cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts) which support estrogen metabolism
Where can I learn more?
- Read Mount Sinai’s synopsis of their estradiol tests.
- National Institutes of Health – Estradiol
- Straight Healthcare – Female Hormone Physiology
DISCLAIMER: IF YOU ARE CONCERNED WITH ANY OF YOUR RESULTS, PLEASE CONSULT WITH YOUR PHYSICIAN.